IPluginEntities
Interface IPluginEntities
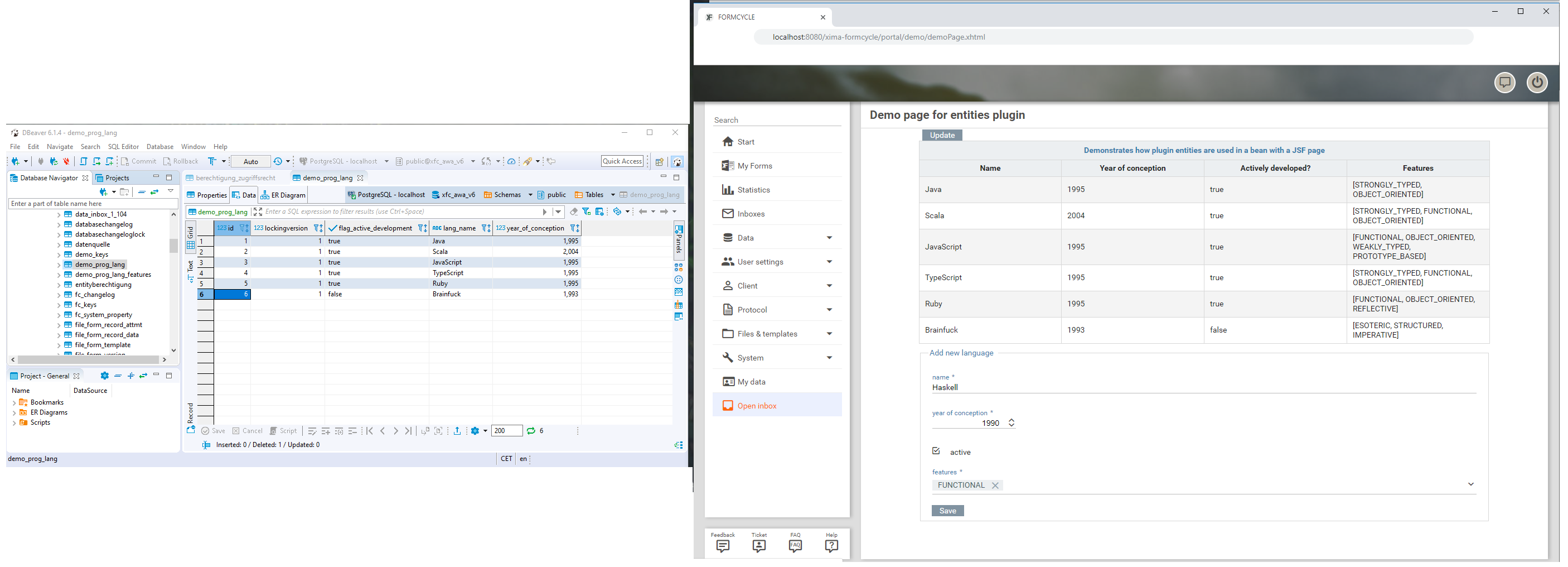
A sample entities plugin that adds a single entity named ProgrammingLanguage. To the left hand side, you can see the new database table that was created in the same database used by Xima® Formcycle. To the right hand side, a simple portal plugin illustrates how this entity can be used. The portal page shows a list of all available programming languages and also lets the user create new languages.
The interface for an entities plugin. This type of plugin lets you add custom JPA (Java persistence API) entities to Xima® Formcycle. You can then use these entities within other plugins, such as IPluginPortal or IPluginFormPreRender. One common use case are portal plugins with or without IPluginMenuEntries that need to save configuration data or a list of items in the database. Please note that plugin entities are not supported on a frontend server - they will work only on a master server.
Each entities plugin consists of the following components:
- one or multiple entity classes that must have the Entity annotation
- a Liquibase script that creates the required database tables and can be used for updates, and
- a DataSource with the connection details to a database (defaults to the FORMCYCLE database)
The entity classes are picked up automatically as long as they are annotated with the Entity annotation.
Use cases
- Save configuration data by portal or another plugin
- Save items required for a portal view
Method signatures
default IPluginEntitiesConnectionRetVal getConnectionDetails()
By default, plugin entities are saved in the system database, ie the same database that Xima® Formcycle uses. In this case, make sure the table names for the plugin entities do not collide with any pre-existing Xima® Formcycle table names. We recommend you add a custom prefix to each table name.
If necessary, you can override this method and return custom connection details for connecting to a different database where you would like to save the plugin entities.
- Return value
- The connection details to the database that will store the plugin entities. If null, the system database of Xima® Formcycle is used.
default List<String> getLiquibaseScripts()
This method may be used to return a list of Liquibase scripts for initializing or updating the database. The Liquibase scripts are run in the order as returned by this method. A Liquibase scripts consists of a list of change sets. Each changeset is responsible for a single logical database modification, such as creating a table or adding some new columns to a table. If an empty list is returned, no Liquibase script are run.
When the plugin is installed for the first time, the scripts are run to create the initial database configuration. Then, when this plugin is updated to a new version and you need to update the database as well, you can add additional change sets to the Liquibase script. All change sets that were run already will not be run again. For this to work, make sure you do not modify any existing change sets, as Liquibase creates a hash of the source code of each change set.
In some cases, your database setup may depend on the version of Xima® Formcycle. If so, and you want to run certain Liquibase scripts only for certain versions, you can check which version of Xima® Formcycle is currently installed via VersionsInfo#sdkVersion.
For more information, refer to the documentation pages of Liquibase.
- Return value
- A list of Liquibase scripts for initializing or updating the database. May be an empty list in case you need to set up the database. Each entry must be a path to a Liquibase XML file, in the format accepted by ClassLoader#getResources.
void onDatabaseReady(IPluginEntitiesParams params) throws FCPluginException
This callback method is invoked after the plugin was initialized and after the database was set up and is ready to be used. You may use the EntityManagerFactory that passed to this method to create new entities or fetch, update and delete existing ones. This is normally done by creating a new EntityManager via EntityManagerFactory#createEntityManager.
However, you may find the API offered by the EntityManager hard to use. If so, you can use the DAO (database access objects) API provided by Xima® Formcycle to work with your entities more easily. First, use IPluginEntitiesParams#getPluginEmManager and save the EM manager in a static field for later use in a bean or a filter. Later, when you need to access the database, use IPluginEmManager#newEntityContext to create a new entity context and pass this context to the methods offered by IAbstractDao. For example, when you have got an entity class MyEntity and want to retrieve a list of all entities:
try (final IBaseEntityContext ec = pluginEmManager.newEntityContext()) {
// use entity context with some DAO
// this fetches all existing MyEntity
new AbstractDao(MyEntity.class) {}.all(null, new QueryCriteriaManager());
}
// use entity context with some DAO
// this fetches all existing MyEntity
new AbstractDao(MyEntity.class) {}.all(null, new QueryCriteriaManager());
}
If you only want to retrieve a subset of entities matching a certain criterion, use the QueryCriteriaManager API offered by Xima® Formcycle. Finally, instead of creating a new DAO on the fly, consider creating your own DAO classes by extending IAbstractDao.
- Parameters
- This method takes the following parameters:
- params
- The parameters this method may make use of. Contains the EntityManagerFactory} for working with the entities, as well as the IPluginEmManager to make that work easier.
- Throws
- This method is allowed to throw the following exceptions:
- FCPluginException
- When this method performs an initial setup, such as creating new entities, and that setup fails. If that exception is thrown, this plugin will be deactivated and not put into service.